Search on Ozon is not only a system for ranking products by their textual relevance to customers' search queries, but also a system for distributing traffic and determining products' quality offers. Both customers and sellers influence search results.
Product position in the search affects its commercial indicators: conversions, traffic, and sales. The way the search is set up allows sellers to influence the position of their products in the search results in a direct, transparent and predictable way. Since quality offers from verified sellers are ranked higher in the search results, they get more traffic and therefore more sales.
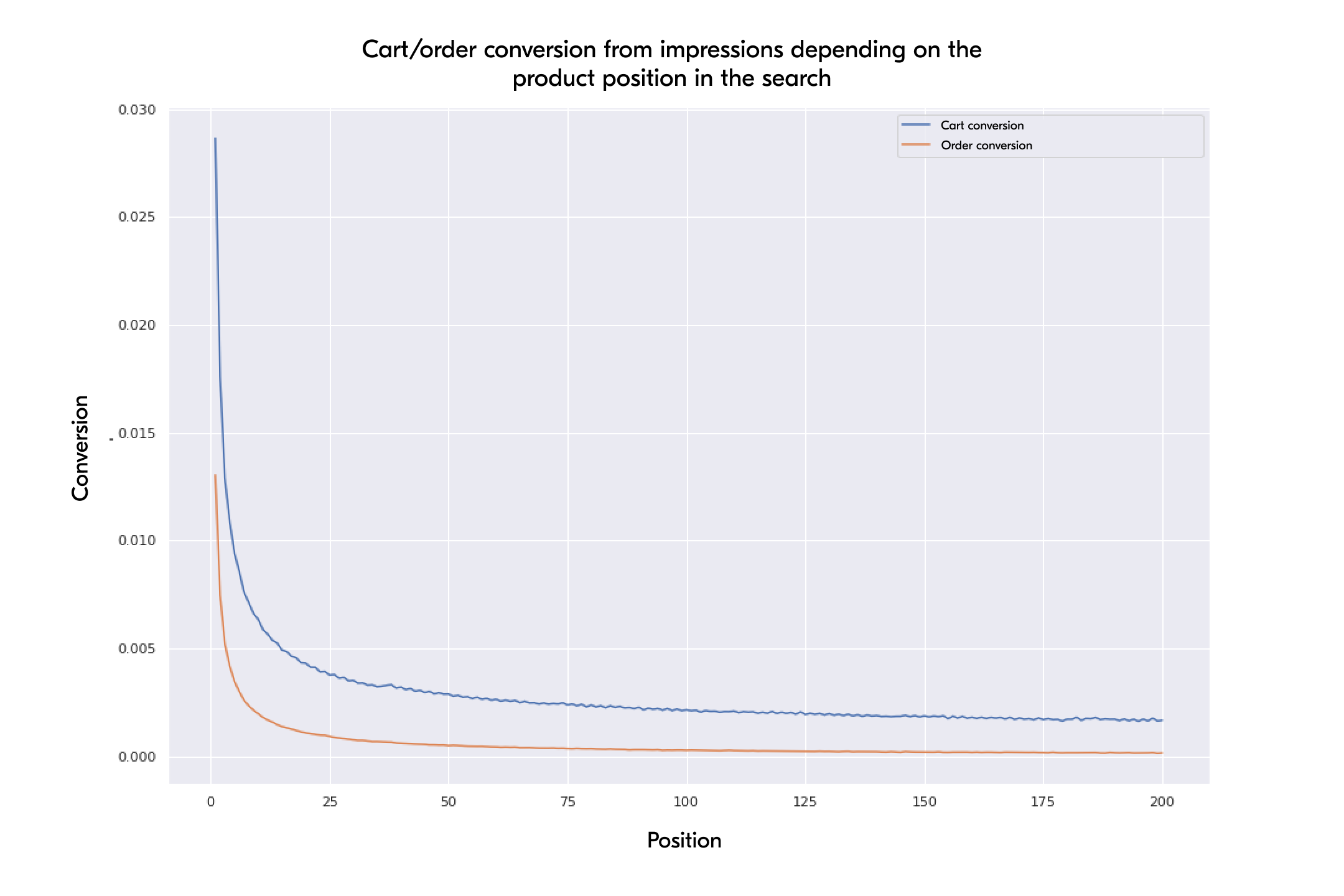
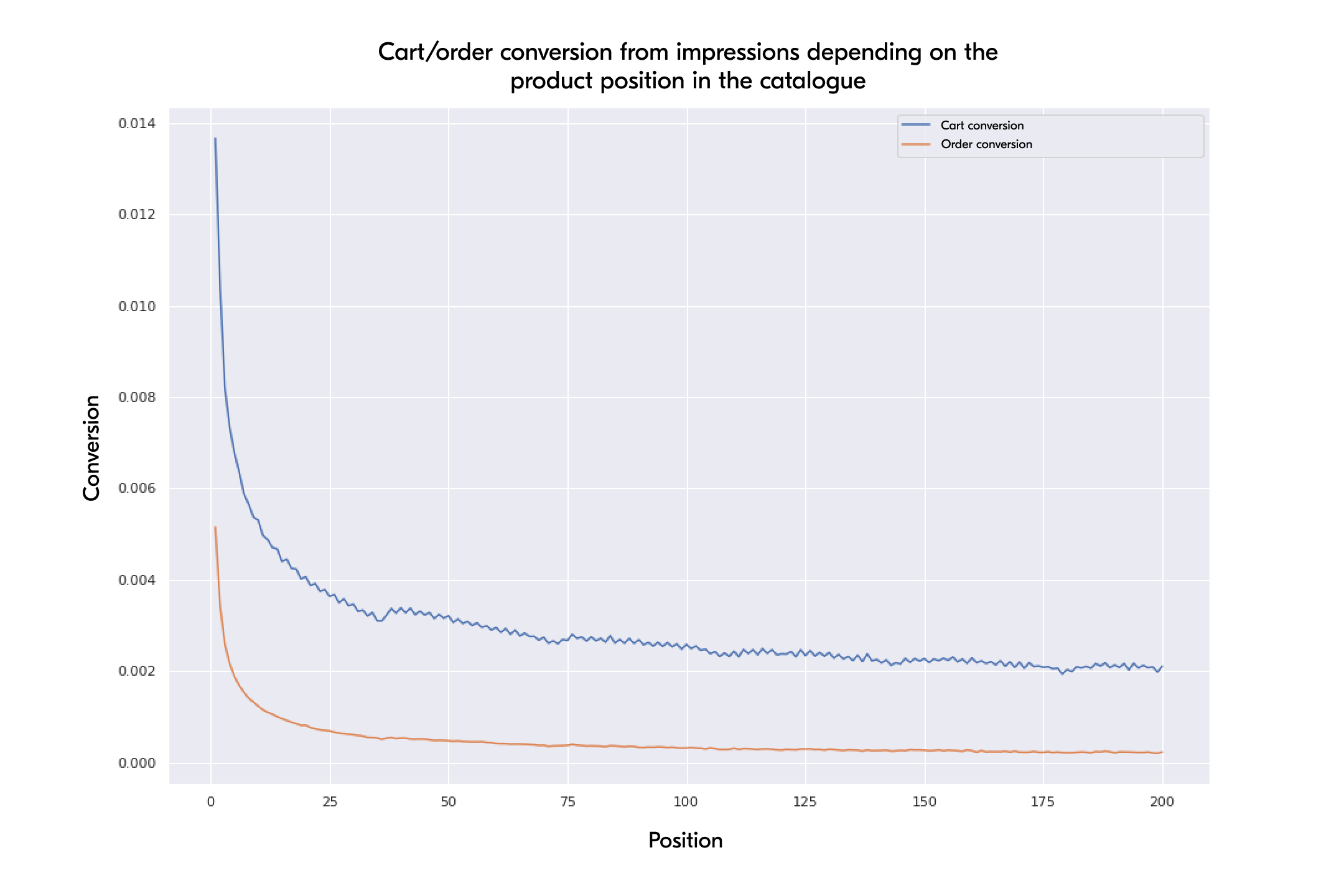
Ozon also determines what a quality offer is based on the product price, its quality, and the delivery speed. For those sellers who can provide such products, Ozon offers free tools for promotion in the search results.
Needs that Ozon search addresses #
- Motivate sellers to make high-quality offers.
- Help sellers demonstrate their products to customers.
- Help customers find and choose the necessary product.
- Take into account the customers' choice when distributing traffic between sellers' offers.
Main principles of Ozon search #
- Inevitability. Search results always react to the actions of sellers or customers.
- Non-discrimination. The reaction of search results to the same actions of different sellers in similar situations is the same.
- Speed. Ozon is actively working to make the search engine response of search results to sellers' and customers' actions fastest possible.
- Transparency. All the details of the search operation on Ozon are open. Ozon doesn’t affect the ranking of products in the search results and doesn’t hide its work principles.
Ozon search scheme #
The process begins as a customer performs a search on the Ozon website. It consists of several stages.
-
Request generation and candidate selection
Every day customers make millions of search queries on the Ozon search engine. To make sure that everyone finds the necessary product among millions of others, at the first stage the search engine generates a large list of candidate products, whose names and various attributes contain words from the search query. For each request, this list can contain up to 500,000 products.
-
Base ranking layer
The search engine sorts the received candidates to sort out 2,000 products with the highest text relevance. If necessary, the range can be expanded, and the engine will load extra 2,000 products.
-
Middle ranking layer
For the resulting list of 2,000 products we now need to estimate the probability with which customers may buy them. The ranking of these products depends on the product features that have proven to be most important to customers in the past. To figure it out, Ozon compares the product features and customer behavior. The result is a score for each product on a scale from 0 to 1.
-
Boosters
Pre-determined increasing or decreasing coefficients are applied to 2,000 products that are ranked from 0 to 1 after the previous stage. For example, a multiplying coefficient can be applied to premium sellers' products, and a decreasing coefficient can be applied to products with a low rating.
-
Displaying products
2,000 products with a final score passed on to the search results. Customers see pages with the products in the specified order. When they have browsed through 2,000 items, the system will load the next 2,000 items.
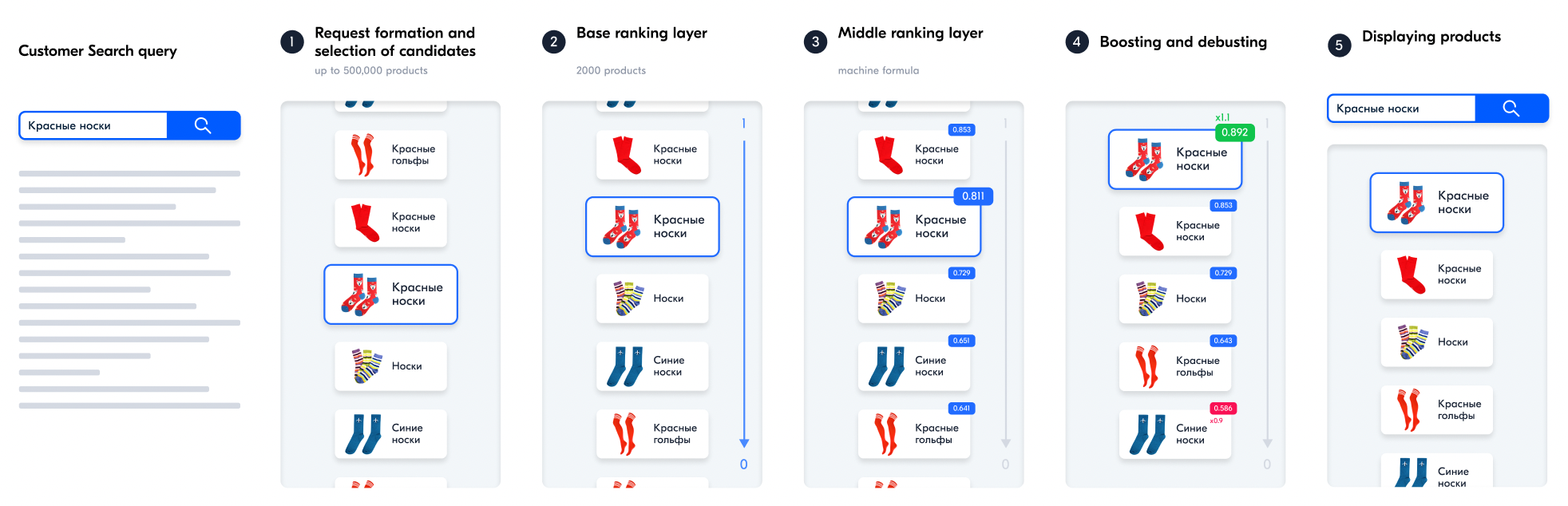
Let’s take a closer look at the search stages.
1st stage: forming a request and selecting candidates #
Search for words by product attributes #
When a search query arrives, the system starts searching for words from this query in all fields and attributes of products that are stored in the search:
- product name,
- product category,
- brand,
- description,
- color, size, material, type and other attributes.
We check several hundred attributes, the final list of them depends on the product category. The more attributes a product has filled in, the easier it is to find it via search.
This list doesn’t include reviews and questions about the product. Therefore, it’s very important for the seller to fill in namely the product attributes: the more fully the product is described, the more likely customers will see it in the search results.
Converting and normalizing a query #
Before selecting candidates, the search engine performs a chain of query transformations to make sure that the suitable candidates won’t be missed:
- Enrichment with synonyms. This step is added to make sure that the query covers more products.For example, so that the “phone” query would return smartphones as a result.
- Request normalization. All the words of the query are brought to a unified form so that, for example, both the “builder Johnson’s emerald ship” and “builder Johnson’s emerald ships” queries would have the same output. At this stage the system also excludes words that don’t carry a semantic load, for example, conjunctions.
- Selection of candidates. All products containing all query words are extracted from the search index for all the remaining words. If the number of such products is too small, all products that contain at least one query word are also retrieved.
At this stage, the search results contain up to 500,000 candidate products. Their list is passed on to the second stage.
2nd stage: basic ranking layer #
Sorting candidates by relevance #
At the second stage, the selected candidates are sorted by text relevance. Here the search engine focuses on:
- The fact of the product’s textual correspondence to the query: at first the number of matches between the words from the search query in the fields and the attributes of the product for each individual word in the query is determined by the usual linear formula. Then the number of matches for all the words from the query is summed up.
- Product rating based on customer reviews. At this stage the rating is used as a multiplying coefficient. The higher the product rating, the higher the coefficient. It ranges from 0% for the minimum rating to 25% for the maximum.
As a result, all candidate products receive an assessment of basic relevance as a combination of text compliance and product rating.
At this stage, the search engine sorts the candidates and passes a list of 2,000 most relevant candidates on to the third stage. If necessary, the range can be expanded, and the engine will load extra 2,000 products.
3rd stage: middle ranking layer #
How ranking works #
At this stage, the search engine needs to evaluate which of the 2,000 products customers are most likely to purchase. Since the probability of buying each product is unknown, you need to predict it to be able to rank the products.
The prediction is made in several stages:
- All the features of each individual product, that may affect the fact of sale, are calculated. Here each feature is a real number. For example, the product rating or its price can be called a feature in this context.
- A machine-trained model is applied to a set of features. It predicts the probability of a sale based on the value of the features. Ozon uses gradient boosting of decision trees as a model.
- The model outputs a number that is used to estimate the product purchase probability.
- The evaluation of the purchase probability of a product is put into the context of the query. The same product will have a different purchase probability for different requests.
How a machine-trained model works #
The purpose of the model is to most accurately predict the product purchase probability based on the product features. Product features contain information about the characteristics of products purchased by customers in the past, and those of them that the ranked product has now.
The model predicts future buying behavior based on this data collected in the past. For example, one of the important factors is the average product conversion to purchase over the last 60 days. For many products it’s possible to state that the product conversion doesn’t change over time. Consequently, the model uses this feature to predict purchase probability, and it’s possible to say that the higher the conversion rate over the past 60 days, the higher the model prediction will be.
The same thing happens with other features — for example, other things being equal, customers prefer products with a large number of reviews, and therefore the more reviews, the higher the prediction of the model will be. At the same time, different features have different predictive power and a different effect on the purchase probability.
The model training is based on using the dependency data between product features and final purchases via a special algorithm. Since many of the features are based on customer behavior, we can say that Ozon customers influence the products' position in search results by their actions. Primarily, the results are influenced by the product’s purchase, as the impact of feature weight on purchase prediction is based on the past sales of the product.
What is taken into account in ranking #
This stage takes into account all the features of the product that affect its sale. These include the product characteristics, its rating, customer behavior, such as placing an order, viewing the product or adding it to the cart. In total, the Ozon search engine takes into account about 100 different features.
Sellers can influence the product position in the search results as they directly control the values of some features.
The main conceptual blocks of the features taken into account:
- Text relevance. This is a property that describes the product’s textual relevance to the query. In the current search model, text relevance has a weight of 20–40%.
- Product sales. This block combines characteristics derived from the past product sales: the product conversion into purchases, and the number of purchases of that product over the last 60 days. Sales weight is 15–25%.
- Popularity by query. This block combines characteristics that describe customer interactions with a product: product impressions, adding it to cart, and to favorites. A product impression is defined as opening the product description card, and viewing the product in the search results. Its weight is 10–15%.
- Personalization. Linking search results to each individual customer, taking into account their purchasing habits, priorities, interests, and other parameters. Its weight is 10%.
- Price. These characteristics are derived from the product price. For example, the current discount size. Its weight is 5–15%.
- Reviews. These are characteristics that are derived from the product rating: the product rating itself, and the number of reviews for the product. Its weight is 5–15%.
- Delivery. This block contains characteristics describing the speed of product delivery: the speed of delivery itself and whether the product belongs to the express category or not. Its weight is 5–10%.
The predictive power of features is fluctuating since both the formula gets updated regularly and new features get added.
At this stage, the search engine evaluates each product from 2,000 candidates on a scale from 0 to 1. The closer the score is to one, the higher position the product will take in the search results and the higher the probability of its sale. All scores are passed on to the fourth stage.
4th stage: applying boosters #
At this stage, increasing coefficients are applied to candidate products ranked from 0 to 1, for example, to products with paid promotion.
How boosting works #
To illustrate the process, we’ll look into the example of the “red socks” query. Let’s say that after passing through three stages of search, ranking included, a product named “red socks” gets a score of 0.7. If this is a product with paid promotion, a booster will be applied to it—for example, × 1,3. In this case, the final product rating will be 0.91 instead of 0.7.
The boosting coefficients change quite often, as Ozon is constantly looking for new coefficients that may help increase the total number of sales on the site.
All boosters, if they aren’t mutually exclusive, are cumulative. For example, let’s consider a product placed on Ozon, that is not only a product with paid promotion, but also has a guaranteed next day delivery, and a good price. Let’s assume that for each of these boosters, the boosting coefficient is 10%. In this case, a product with a machine training based relevance score of 0.7 will get a final relevance score of 0,7 × 1,1 × 1,1 × 1,1 = 0,9317.
Booster types #
The following boosters are applied after the model ranking and are currently enabled:
- Promotional boost stands for the purchase of a boosting coefficient for a price. Learn more in the Promotion → Promotion in search results section of your seller account.
- Logistics boosters raise product position by 25%. A product can have only one booster from this category:
- realFBS Express,
- Ozon fresh,
- domestic warehouse: products stored in Ozon warehouse that’s located in the customer’s region and works under the FBO scheme.
- Delivery speed boosters depend on how fast the product is delivered to the customer:
- in 1-2 days: the product raises in search results;
- in 3 days or more: the product drops in search results.
- Big Ozon promotions. For example, “Marathon of discounts”, “11.11 Sale”, and “Black Friday Sale”. The coefficient depends on the sale.
- Boost of products with favorable or moderate price index. The coefficient depends on the price and subscription.
- 5% for moderate index,
- 7.5% for favorable index,
- 10% for favorable index with Premium subscription,
- 12.5% for favorable index with Premium Plus subscription.
Resulting score and the effect of boosting #
Boosting may not be sufficient to supersede the effect of customer voting.
For example, let’s consider two products, one of which after the third search stage has a score of 0.9, and the other has a score of 0.6. In this case, the first product should be ranked first in the search results, and the other should be ranked second. If the second product is boosted × 1.25, its resulting score will be 0.6 × 1.25 = 0.75. Since the initial score of the second product was rather low, boosting still won’t help it rise above the first product in the search results.
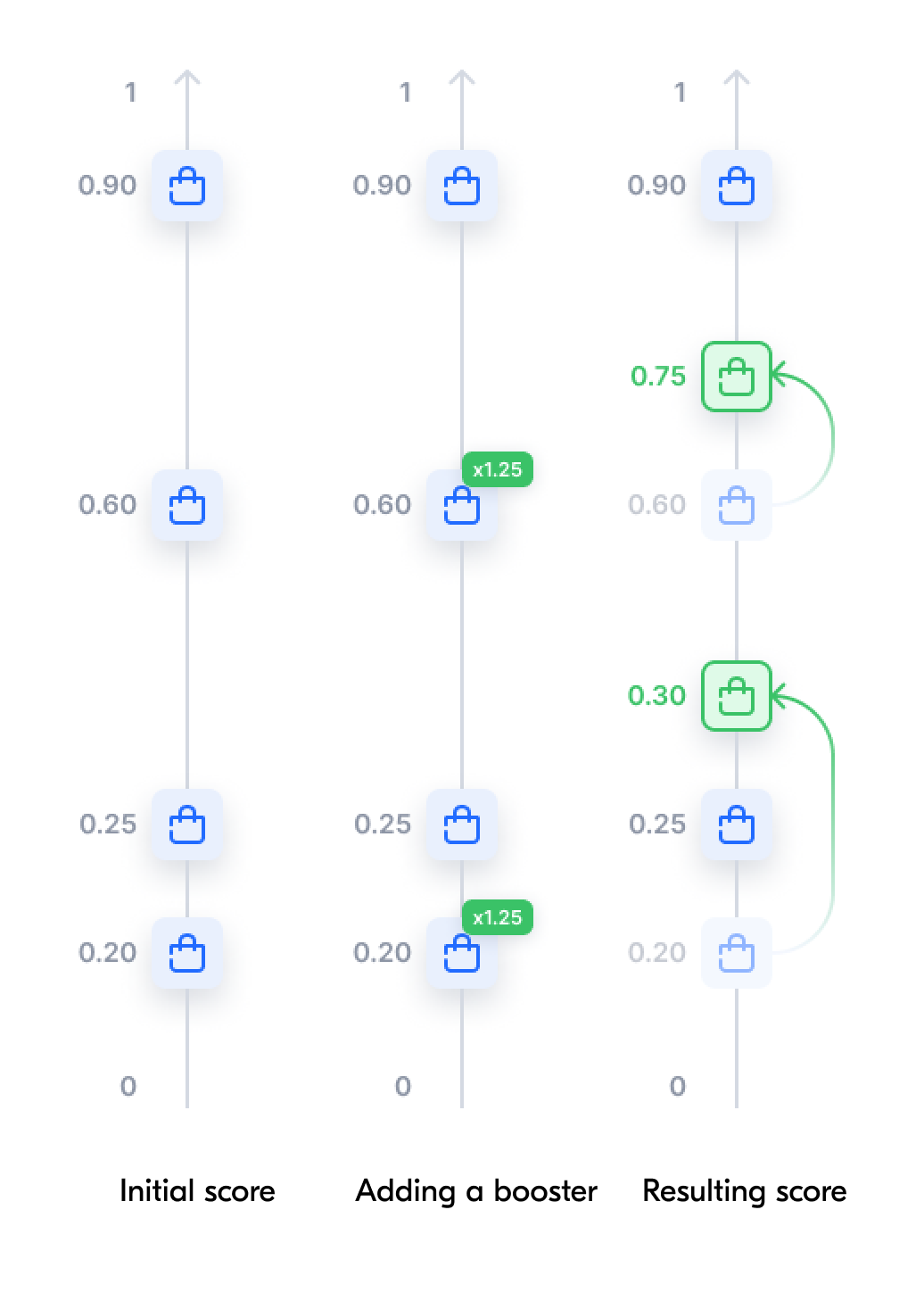
For one query the final score of 0.9 can get the product to the first position, and for another it’ll bring it to the tenth one only. It depends on the score of other products included in the search results.
5th stage: displaying products #
How the product display works #
- The search engine gets a list of 2,000 products with final scores.
- The products are displayed to customers based on these scores: the ones with the highest scores appear at the top of the search results list, and the ones with the smallestshow up at the bottom.
- In both desktop and mobile versions of Ozon website the search results page where products are displayed consists of 36 tiles.
- In the mobile app, the first 36 products are shown on the first screen, and the next ones are loaded when scrolling further.
- The products in the search results are loaded along with their most up-to-date characteristics and images.
The product’s place in the search results affects its commercial indicators: conversions, traffic, and sales.
How to raise the product in the search results #
-
Use the search promotion. You can affect your products position on the search page or in the catalog by setting rates for them for the necessary search queries. To set a rate, navigate to the Promotion → Promotion in search results section of your seller profile.
-
Collect customer reviews. The higher the product rating and the more reviews it has, the higher the product appears in the search results. You can offer customers points for submitting reviews of your product. To enable this service, go to the Products → Reviews for points section of your personal account.
-
Fill in the product attributes completely. The more information about the product you add, the easier it is for your customers to find it via search. To edit product details, go to the Products section and choose the Edit product option on the necessary product. You can also edit information for several products at once using an XLS template.
Frequently Asked Questions #
I created a product and specified its quantity in stock. I can see this product on the Ozon website when I go to its page using a direct link, but it doesn’t appear in the search results. What should I do? #
New products don’t get into the search results immediately—as a rule, it takes several minutes. Besides, the product may not be visible in the search results for 20 minutes after the changes are made due to the peculiarities of search results caching. If the product is still not shown in the search results after this time has elapsed, please check whether all the key product details are filled in: namely its price, name, and description. If the product doesn’t appear in the search results within 48 hours, contact the support service.
My product doesn’t appear in the search results for the queries where I expect it to appear. #
If the product isn’t visible by the specific query, please make sure that:
- The product really doesn’t show up in the search results: the search results can contain up to several thousand products, and your product can appear anywhere on this list. To make certain that the product isn’t in the search results, use the corresponding filters, for example, by brand or price. This will reduce the selection.
- Whether the product will be located if you remove the category prediction. If the category prediction is triggered, the Search everywhere button appears next to the title under the search bar. In this case, please check whether the product belongs to the predicted category and whether it should belong to it.
- The product isn’t merged into a single product tile with other products in the search results. Check if there are different attribute options on the product tile, such as color, size, or number of pieces.
- The product isn’t found when searching for synonyms of the search phrase.
If you have performed all the actions above, and the product still doesn’t appear in the search result, please contact Ozon support team.
Is it possible to artificially increase the indicators to raise my product in the search results? #
Many of the above indicators can really be increased artificially. It can be done either by fair means, for example, by purchasing high-quality external traffic, or by unfair ones, for example, by purchasing bots.
Using bots won’t help you raise the product in the search results as the ranking is determined by customer behavior. For example, you can increase impressions via bots. However, if the product has a lot of impressions, but the number of its sales is low, this means that customers don’t like this product much. It can negatively affect the product ranking.

